Scientific quality of the participants
The roles given to the STRAVAL partners correspond to their expertise and transnational/EU project experience. On this basis, the activities have been distributed accordingly to ensure their completion. The consortium is established in an interdisciplinary and complementary way (Academia – Enterprise) in order to combine the best of existing expertise in the required fields in both, EU and LA countries.
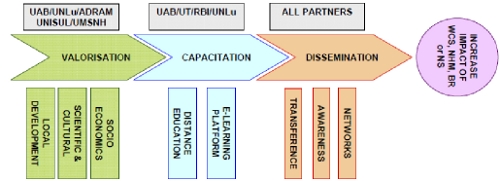
Complementarities/synergies between the participants The value chain of STRAVAL, given in the following figure, involves a series of phases and activities, in which the members of this consortium present a high expertise degree (in terms of Transnational/EU project experience) and a long-lasting cooperation as it is demonstrated by the high number of joint activities.
Relevance of the proposed partnership to the area of collaboration
In the case of Argentina, the Agreement in S&T cooperation in the environmental thematic area has been among the most dynamic in FP6, both in the thematic priority (9 projects, 12 participations) and under INCO (8 projects with 11 participations). Reconciling multiple demands on coastal zones and marine research, water management, biodiversity and climate were principal themes addressed in ongoing collaborations, on which future cooperation should build. Concerning the partnership with Brazil, there is an agreement with EU in terms of Science and Technology. Its science and technology component identifies priority areas of cooperation such as Food, Agriculture, Fisheries and Biotechnology; Social Sciences and Humanities; E-Infrastructure; Energy; Cross-Sectional Studies, Training and Development of Human Resources, Researcher Exchanges; Environment and Climate Change; Nanotechnology and Materials; Health; Safety; Information and Communication Technologies and Transport. The Joint Action Plan was adopted in 2009. In relation to these cooperation areas, STRAVAL fullfils some of the priority areas due to the training of human researchers and the environmental research related to the socioeconomical impact of cultural heritage identified sites. Regarding Mexican partnership, the Country Strategy Paper 2007-2013, that currently guides bilateral cooperation between the European Union and Mexico is valid for the 2007-2013 period. It has the main objective of reinforcing and expanding the cooperation programmes from the past period. It aims to support Mexico in consolidating its developmental process. Three important sectors for bilateral cooperation are addressed such as Social Cohesion, Competitiveness and Economic Development and Education and Culture.
CAPACITIES (EXPERTISE, HUMAN RESOURCES, FACILITIES, INFRASTRUCTURE) TO ACHIEVE THE OBJECTIVES OF THE PLANNED COOPERATION
PARTNER 1: DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY – DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY / UNIVERSIDAD AUTONOMA DE BARCELONA (UAB) / SPAIN
Description of Legal Entity: The Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (http://www.uab.es/) was founded in 1968 and has 30,406 undergraduate students, 4,657 graduates, 12,426 postgraduate and continuing education students, 2,346 foreign students; 3,431 teaching and research staff, 2,504 administration and services staff, and offers 78 undergraduate courses, 334 postgraduate and continuing education programmes, 183 masters degrees, 88 doctoral programmes. There were 372 PhD dissertations in 2007. During FP7, 15 Marie Curie fellows have been hosted in UAB. Trained personal actively collaborates with departments and the central government in managing the PEOPLE program and the reception of fellows. UAB has an International Welcome Point which helps researchers/students, as well accommodation in the campus (Vila) and other miscellaneous services, restaurants, shops, sport activities services, etc… The UAB is recognised around the world for its quality and innovation in research and as a coordinator of a potent scientific and technological centre (the Esfera UAB). Thanks to its activities in promoting, directing and projecting newly acquired knowledge towards its socio-economic surroundings, the UAB has become a forerunner in quality researchers and already has received 50 Awards for Quality from the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science, being one of the five Spanish universities with the qualification of Campus of Excellence. The Vallès Synchrotron will be functioning in 2011, close to the UAB, on the Vallès Technological Park. Recently UAB has opened an International and Promotional Office in Shangai and Seoul.
Department/Institute involved: The Unity for Crystallography and Mineralogy of UAB, integrated to the Department of Geology focuses his research in materials science and geochemistry & environmental geology and has participated in different projects financed by Research Directorate General (DG RTD) on new materials with applications in water purification (TOXMET) cultural heritage conservation (TRAINMONHER), environmental projects (SOWAEUMED, Anthropol.Prot) and political projects (EULASUR, EUCARINET, EUMEXCyT). Within the Chemistry Department, the Research Group of Separation Techniques in Chemistry, GTS, is a “Consolidated Group of Quality Research” since 1993 and from 2002 belongs to the “Xarxa IT” of Industry Department of Catalonia Generalitat. GTS has developed its activity during the last sixteen years in both basic and applied aspects of separation science and technology participating in different projects financed by Research Directorate General (DG RTD). The research is currently addressed to develop new concepts in process separation and to problem-solving applications. Thus, different separation techniques are applied to a great variety of situations including environmental research, biomedical and agrofood applications and analytical processes. Available techniques and methods for material characterisation: electron microscopy, X-ray fluorescence, X-ray diffraction, ICP mass spectroscopy, atomic absorption, optical microscopy, image treatment.
Description of Legal Entity: The University of Tartu was founded as Academia Dorpatensis (Gustaviana) in 1632. UT is Estonia’s leading centre of research and training. It preserves the culture of the Estonian people and spearheads the country’s reputation in research and provision of higher education. As Estonia’s national university, UT stresses the importance of international co-operation and partnerships with reputable research universities all over the world. The robust research potential of the university is evidenced by the fact that it is the only Baltic university that has been invited to join the Coimbra Group, a prestigious club of renowned research universities. UT includes nine faculties, five colleges and several regional development units, of which the latter two are situated in different parts of Estonia. To support and develop the professional competence of its students and academic staff, the university has entered into bilateral co-operation agreements with 48 partner institutions in 19 countries. The university employees 3500 people of whom approximately 50% are members of the academic staff (including 180 professors), the number and proportion of academic employees are increasing. The proportion of full-time teachers and researchers holding a PhD was close to 65%. There are a total of 17,400 students studying at the university. Their number includes over 500 visiting and international students. The number of doctoral students is 1250, with 80-90 doctoral defences taking place each year.
Department/Institute involved: The Department of Geography, Institute of Ecology and Earth Sciences covers at present research and education in all fields of modern geography such as physical geography, landscape ecology, geo-informatics, cartography, and human geography. The Chair of Physical Geography and Landscape Ecology is teaching both traditional disciplines of physical geography, landscape ecology and ecological engineering. Scientific research is carried out in the fields of nutrient fluxes in landscape, changes in landscape, climate and related hydrological processes, constructed and natural wetlands etc. The Chair of Human Geography and Regional Planning has also a wide area of research from mobile positioning studies of real-time geography studies to demographic processes and regional planning issues. The Chair of Geo- informatics and Cartography is active in the field of GIS-based landscape- and regional-level modelling of various natural and socio-economic processes, as well as remote sensing and earth observation methods. Wide co-operation with other research institutions, local authorities and state departments both in Estonia and worldwide is an essential part of everyday activities.
PARTNER 3 RUDER BOSKOVIC INSTITUE – Laboratory for Measurements of Low-level Radioactivity, Zagreb, CROATIA
Description of Legal Entity: The Ruđer Bošković Institute (http://www.irb.hr/en/) is the largest Croatian research centre for basic sciences, participating also in science applications and higher education. The multidisciplinary character of the Institute is reflected through the different research fields in physics, chemistry, oceanography (including marine and environmental research and geosciences), biology, biomedicine, computer science and electronics/engineering. Its mission is determined in three main directions: (i) production of high-quality fundamental research, (ii) involvement in higher education and (iii) contribution to the growth of the national economy through production of new technologies based on our own IP and expertise. Recently new techniques have been introduced: preparation of graphite targets for measurement of 14 C activity by accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) and the enrichment for tritium activities measurements by liquid scintillation counting (LSC). Within the European Union the RBI forms a part of the ERA, actively participating in FP since 2002. At the moment there are twenty FP6 and 4 FP7 running projects, successfully managed by RBI researchers.
Department/Institute involved: The Laboratory for Measurements of Low-level Radioactivity at the RBI is a part of the Division of Experimental Physics. The group studies radioactive isotopes of carbon (14C, radiocarbon) and hydrogen (3H, tritium) with emphasis on development of measurement techniques and applications in archaeology, geology, hydrology, environmental sciences, geochemistry, and paleoclimatology. The Laboratory is involved in radiocarbon dating, tritium activity measurement in natural waters, the use of stable isotopes (2H, 13C, 18O) together with the radioactive ones (3H, 14C) in hydrogeological, paleoclimatological and ecological studies. The Laboratory performs up to 400 radiocarbon analyses and about 250 tritium analyses per year. The main scientific research has been financed by the Ministry of Science, Education and Sports of the Republic of Croatia within the presently running project “Natural radioisotopes in karts studies and dating”. During the last 30 years the Laboratory has taken part in numerous international projects, mostly financed by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in Vienna, as well as by the National Science Foundation (NSF) in USA, and European Commission within the FP5 and FP6.
PARTNER 4 DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCES THE NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF LUJÁN (UNLU) / ARGENTINA
Description of Legal Entity: The National University of Luján (www.unlu.edu.ar) is developing an important and growing activity in the 40 municipalities of its territory of Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. UNLu has 157 different research projects which encompass different areas of knowledge such as Environmental studies, Biotechnology, Applied Physics, Applied Microbiology and Mathematics, Agronomic Sciences, Genetic, Food Science and Technology, Applied microbiology, Lactic Bacteria, Management of the Patrimony and Sustainable Tourism Teledetection, Animal and Vegetal Production amongst others. In the technological and innovation management field, UNLu has been a pioneer in Argentina with the start of its assistance centre (CATEC) in 1993 and later with the first innovating companies incubator (INCUEI) in the country in 1997. From its EMPRENDEDOR programme different modalities of liaison between University and Industry have been covered. This allowed UNLu to receive in 1999 the National Prize “José Balseiro”, awarded for its successful works.
Department/Institute involved: The Department of Social Sciences (www.unlu.edu.ar/~sociales/) offers academic services to most of the races of the UNLu, in the totality of the Seats and Regional Centres. The activities of teaching and investigation are organized from the Divisions that, at the present time, are the following ones: Administration, Trade International and Marketing, Law of Right, Economy, Epistemology and Methodology, Geography, History, Countable Information and Social Work The main lines of investigation that are being developed in the Department include/understand thematic such as history and economic, social and demographic structure of the region and the province of Buenos Aires; management of the innovation and the knowledge, management of the patrimony and sustainable tourism problematic environmental, problematic of the woman, health and feeding, among which we can mention. So far the UNLu team has participated of the advisers group who designed and consolidated the approval of the First Law of Science, Technology and Innovation of the Buenos Aires Autonomous Government, and has experience as the regional coordinator of International Cooperative Projects, in the FP, such as UNIND-LAM (FP5 http://www.unind-lam.uvsq.fr), UNIVEMP-LAM (FP6 www.univemp-lam.net/homeen.html), EULASUR (FP7 www.icmab.es/eulasur)
PARTNER 5: AGÊNCIA DE DESENVOLVIMENTO REGIONAL DA AMUREL – ADRAM.
Description of the legal Entity: founded in 2003 by the Universidade do Sul de Santa Catarina (UNISUL), the Associação Empresarial de Tubarão/SC (ACIT), the Instituto Euvaldo Lodi/Federación das Industrias do Estado de Santa Catarina (IEL/FIESC), the Serviço Brasileiro de Apoio à Pequena e Media Empresa (SEBRAE), the Associação dos Municipios da Região de Laguna/SC (AMUREL) and the Associação do Comércio e da Indústria do Vale do Braço do Norte (ACIVALE), is a non-for-profit institution, recognized by the Minister of Justice as a Social Organization of Public Interest (OSCIP). The main objective is local and regional development, research institution in technical areas as an innovation, industry, entrepreneurship and social assistance of population in risk areas. Have more than 30 researchers in areas such as social security, social and economic development, entrepreneurship, tourist promotion and environment issues. Now is already principal consultant institution for the local government in areas such as Housing Plans of Social Interest (Municipalidade de Jaguaruna/SC), Municipal Health Fund (Municipalidade de Santa Rosa de Lima, Braço do Norte, Armazem, etc.), Local Development Plan (Municipalidade de Tubarão). In 2009 has acted as regional coordinator for the Course for Entrepreneurship in Biotech, organized by the Mercosur-UE Biotech Program (BIOTECSUR). Also was regional coordinator for the UNIVEMP-LAM project founded by the UE, and partner in the AECID Project of Creation of Referential Institute in Diagnostic, Remediation and Evaluation of Polluted Areas, in cooperation with the UAB and UNISUL. Also has the presidential chair for the Tourist Governance Forum for the South of Santa Catarina State (Brazil).
PARTNER 6 UNIVERSIDADE DO SUL DE SANTA CATARINA/FUNDAÇÃO DE APOIO À EDUCAÇÃO, PESQUISA E EXTENSÃOUNISUL / BRAZIL
Description of the legal Entity: Created in 1964, appeared in Jaws as FESSC, the Education Foundation of Southern Santa Catarina, becoming university in 1989. As University is focused on preparing the new generations, feeding their commitment to society and their new values. Among its main objectives is to consolidate as a means of innovation and ongoing support to change society, investing in partnerships and alliances with a participatory management model which has guaranteed the quality and efficiency. UNISUL has four camps in Shark, Araranguá (1992), Palhoça (1996) and Florianópolis (2002), with units in several cities. Has 24273 students, 1471 teachers and 805 staff, distributed in more than 50 undergraduate, graduate, distance learning (with regular programs in OAS, Organization of American States and UNESCO), and 2 expertise recognized by CAPES. UNISUL, is consolidating its position as one of the most innovative and entrepreneur Brazilian universities. The classical concepts of university – development, policies and guidelines – are carefully combined with the advanced business concepts – organization’s overall strategy, planning and strategic action.
Department/Institute involved: The Technology Centre Unisul (CENTEC) is installed in an area of 8,400 m2. Provides full support to teaching – in the development of experimental classes, contextualizing theory and practice, research, designing and developing projects/programs. The link between the University and Regional Community also occurs through analytical services, testing, consultancy and technical consultancy, as well as plans and partnerships for technical cooperation and institutional environmental agencies, public and private companies, municipalities, and other services provided in various areas of knowledge. Materials Laboratory and soils located next to CENTEC (Technology Centre) have the physical space, equipment and human resources for service in the area of construction. Perform qualification tests of steel, red ceramic (ceramic bricks, tiles), aggregates for concrete and mortar and qualification tests of soil deposits. Develops four concrete and mortar. Performs service with companies in the manufacturing of prefabricated (tiles and concrete blocks). Performs testing in situ permeability and degree of soil compaction. Performs collection and casting of test specimens of concrete. Practical classes held in the disciplines of building materials, strength of materials, soil mechanics, building construction and structures. Laboratory Physicochemical and microbiological/atomic absorption spectrophotometer Performs analysis pH, turbidity, conductivity, colorimetric, volumetric, gravimetric, nitrogen, oil and grease, total and fecal coliforms, BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) and COD (chemical oxygen demand) in samples such as ceramics, minerals, water effluents, wastes and environmental/pollution studies in general. Digested solids and liquids for analysis of metals and non-metals.
PARTNER 7: MATERIALS DEPARTMENT, CIVIL ENGINEERING FACULTY, UMSNH, MORELIA, MICHOACÁN, MÉXICO
Description of the legal Entity: Universidad Michoacana de San Nicolás de Hidalgo is a public university in the state of Michoacan, based in Morelia, Michoacan, Mexico. It was founded as the College of St. Nicholas,”Bishop” in Basque de Quiroga Patzcuaro by en 1540. This is the most important educational institution of the State of Michoacan, one of the largest public universities in the country. It now has several colleges and campuses in the cities of Apatzingan and Uruapan. The UMSNH has approximately 45000 students enrolled in the different levels from bachelor, degree, masters and doctorate; its academic plant is of almost 5000 professors, mostly from Michoacan state, but also houses students of the states of Guanajuato, Guerrero, Colima, Chiapas, Tabasco and Jalisco State. One of the main strengths is currently the Graduate program, which now offers more than forty graduate programs between masters and doctorates, most of which are recognized in the NPP (National Program graduate) from CONACYT.
Department/Institute involved: The Faculty of Civil Engineering was the third school founded in UMNSH after the faculties of Law and Medicine in 1930. Mexican Civil Engineering has recognized prestige. It has 60 full time academic, 2 part-time, has 1,500 students enrolled in undergraduate level and has 3 master’s programs included in the National Register of Postgraduate Excellence in the areas of Highways, Structures and Environmental Sciences, a doctoral degree in civil engineering is formalizing. The Faculty has 9 Academic Departments: Environmental Basic Sciences and Mathematics, Structures, Humanities, Construction, Hydraulics, Materials, Surveying and Land Transportation. The Department of Materials has the Laboratory “Ing Luis Silva Ruelas” and the Geology Museum “Dr. Genaro Gonzalez Reyna”, as well as the first and only consolidated academic body of the Civil Engineering Faculty. CAC-UCD-147 made by Elia Mercedes Alonso Guzman, Wilfrido Martinez and Fernando Augusto Velasco Molina Avalos, with academic partners: Cindy Lara Gomez Hugo Luis Chavez Garcia.